A Beginner's Guide to the Aseptic Filling Process
leading paragraph:
Confused about aseptic filling? Let's break it down simply!
snippet paragraph:
Aseptic filling is a process where sterilized food or beverage products are filled into sterilized containers in a sterile environment. This ensures the product remains safe and shelf-stable for extended periods without refrigeration.
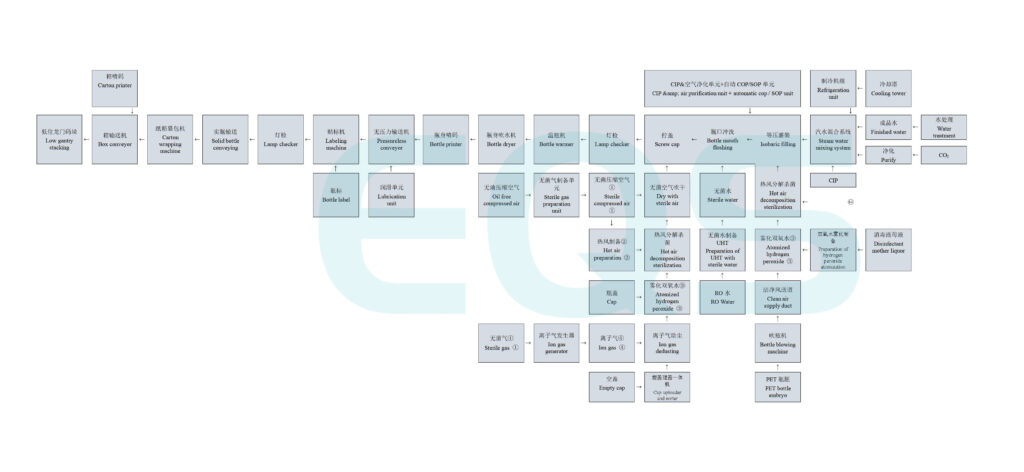
Transition Paragraph:
Let's explore the key steps involved in this fascinating process.
What is Aseptic? Understanding the Basics
leading paragraph:
What does "aseptic" really mean? Let's clarify!
snippet paragraph:
"Aseptic" means "free from harmful bacteria, viruses, or other microorganisms." In aseptic filling, the goal is to keep the product and packaging completely sterile throughout the entire process.

Core Principles of Aseptic Filling
- Sterility: Absence of harmful microorganisms.
- Prevention: Preventing contamination.
- Control: Maintaining a sterile environment.
- Hygiene: Minimizing risks.
- Safety: Ensuring product quality.
- Quality: Delivering safe products.
Dive deeper Paragraph:
At its core, the term "aseptic" refers to a state of being free from harmful bacteria, viruses, or other microorganisms. In the context of aseptic filling, this means that both the food or beverage product and the packaging materials must be completely sterilized before they come into contact with each other. The entire filling process must then be carried out in a sterile environment to prevent any contamination from occurring.
Step 1: Sterilizing the Product
leading paragraph:
How do they make sure the food or beverage is completely sterile?
snippet paragraph:
The product is typically sterilized using ultra-high temperature (UHT) processing. This involves heating the product to a high temperature (e.g., 135-150°C) for a short time (e.g., 2-5 seconds) to kill any microorganisms.
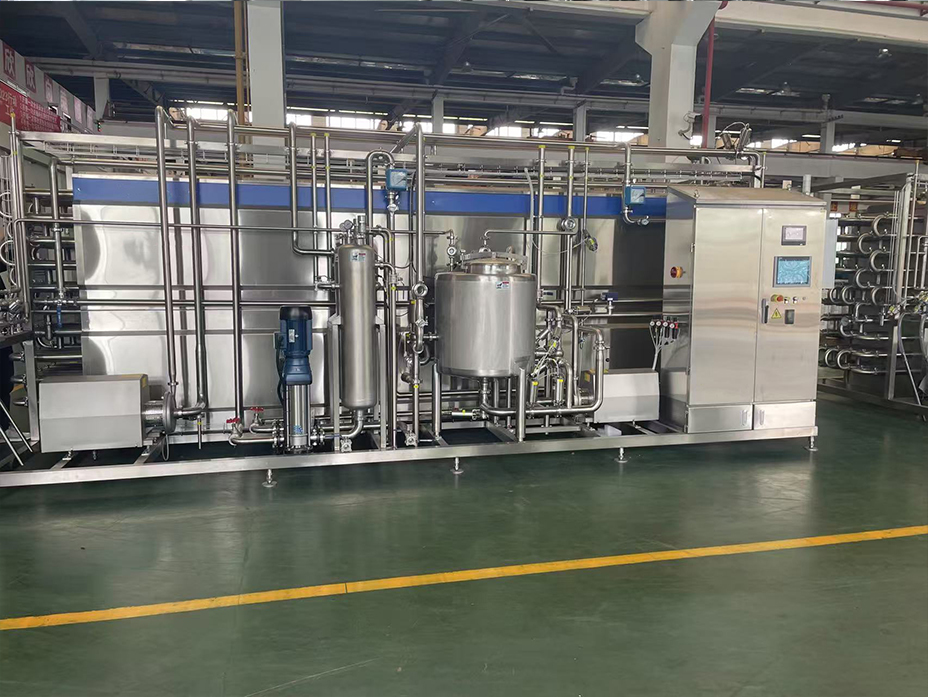

UHT Explained
- High Heat: Eliminates bacteria.
- Short Time: Preserves flavor.
- Rapid Cooling: Maintains quality.
- Continuous System: Efficient output.
- Precise Control: Maintaining temperature.
- Effective Sterilization: Ensuring safety.
Dive deeper Paragraph:
The first critical step in the aseptic filling process is to sterilize the food or beverage product to eliminate any microorganisms that could cause spoilage or pose a health risk to consumers. Ultra-high temperature (UHT) processing is the most common method used for sterilizing liquid food products in aseptic filling. This process involves rapidly heating the product to a high temperature, typically between 135°C and 150°C, for a short period of time, usually between 2 and 5 seconds.
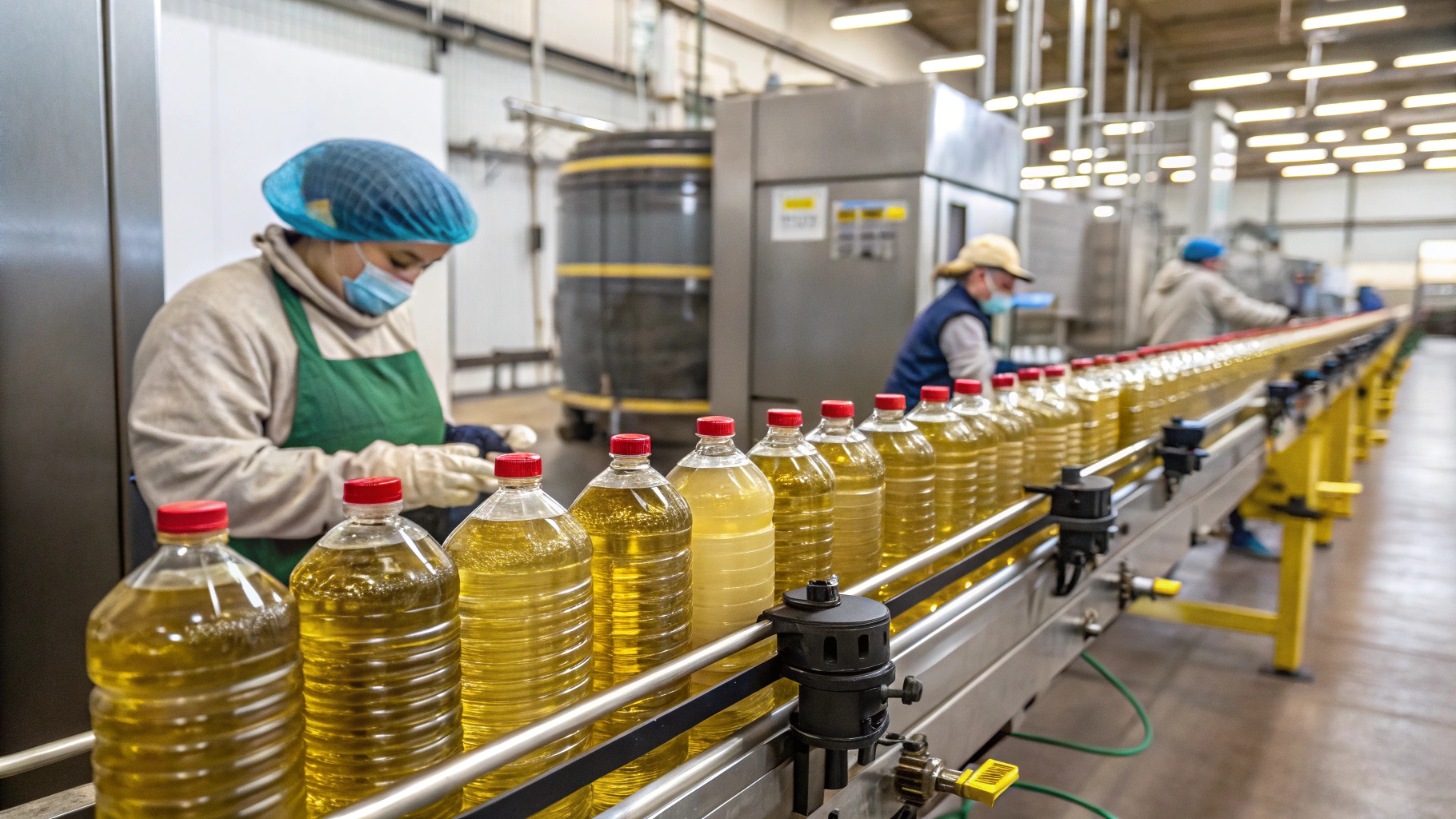
Step 2: Sterilizing the Packaging
leading paragraph:
What about the containers? How do they get sterilized?
snippet paragraph:
The packaging (e.g., bottles, cartons, pouches) is also sterilized using various methods, such as chemical sterilants (e.g., hydrogen peroxide), heat, or radiation. This ensures the container is free from any microorganisms.
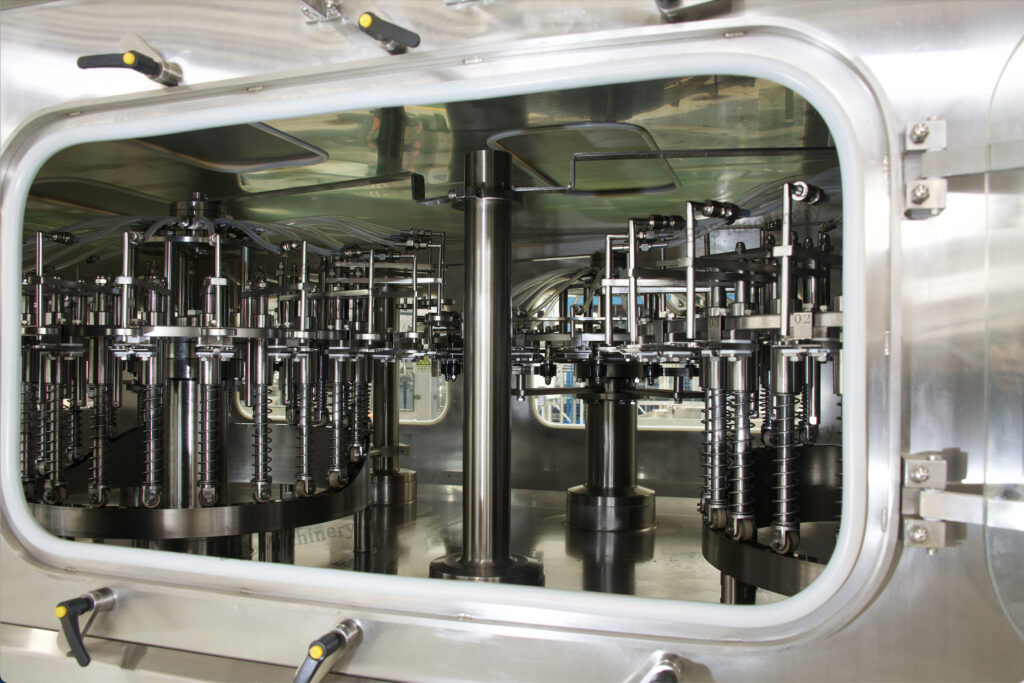

Packaging Sterilization Options
- Chemical Sterilants: Hydrogen peroxide is common.
- Heat: High-temperature exposure.
- Radiation: UV or electron beam.
- Rinsing Systems: Removing sterilizing agents.
- Air Filtration: Maintaining a sterile environment.
- Automated Monitoring: Ensuring effectiveness.
Dive deeper Paragraph:
In addition to sterilizing the food or beverage product, it is also essential to sterilize the packaging materials to ensure that they are free from microorganisms that could contaminate the product during the filling process. Various methods are used to sterilize packaging materials, depending on the type of material and the specific requirements of the product. Chemical sterilants, such as hydrogen peroxide, are commonly used to sterilize packaging materials like plastic bottles and cartons.
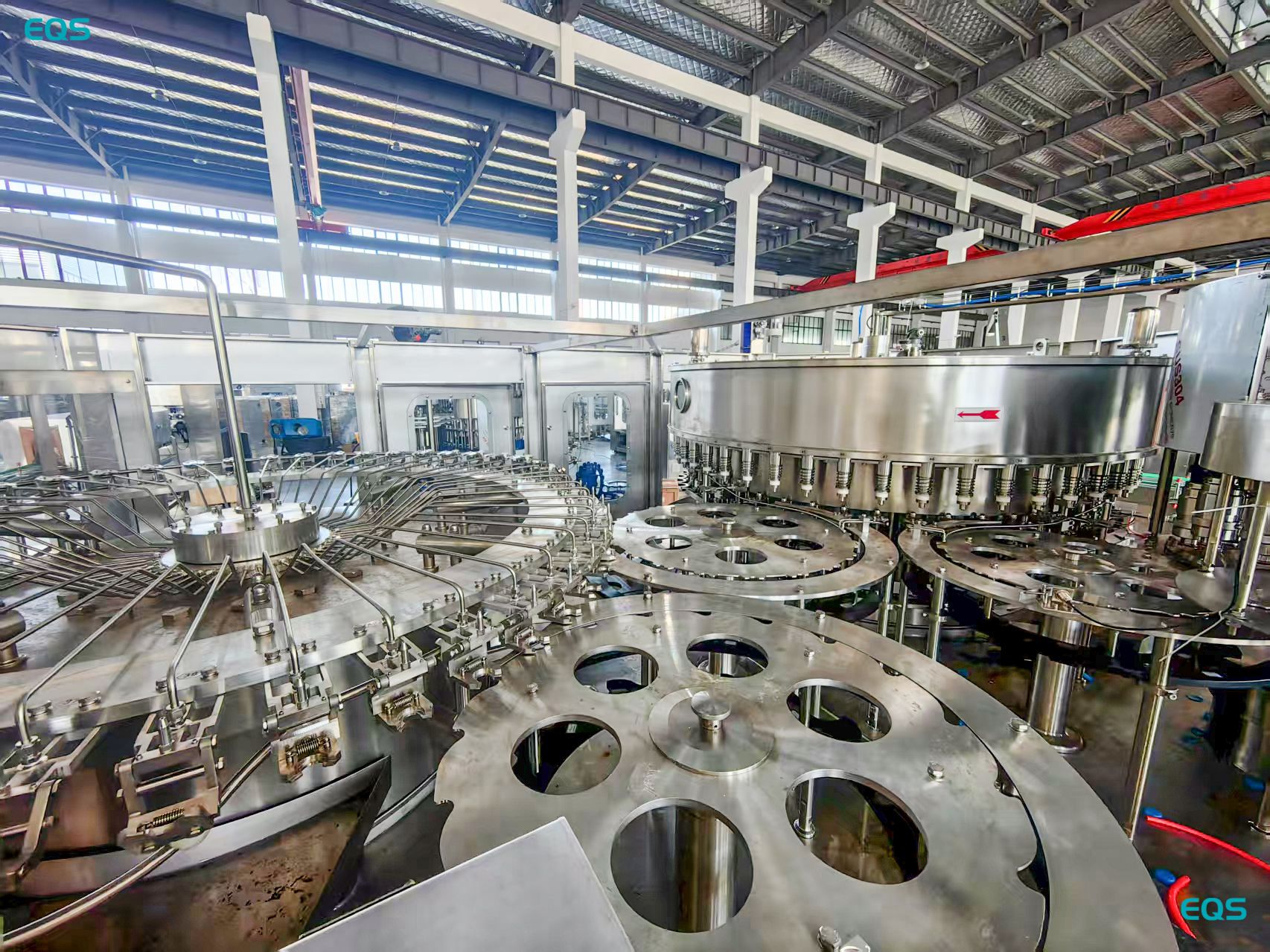
Step 3: Filling in a Sterile Environment
leading paragraph:
How do they combine the sterile product and container without contamination?
snippet paragraph:
The sterilized product is filled into the sterilized container within a sterile environment, typically a closed chamber with HEPA-filtered air. This prevents any microorganisms from entering during the filling process.
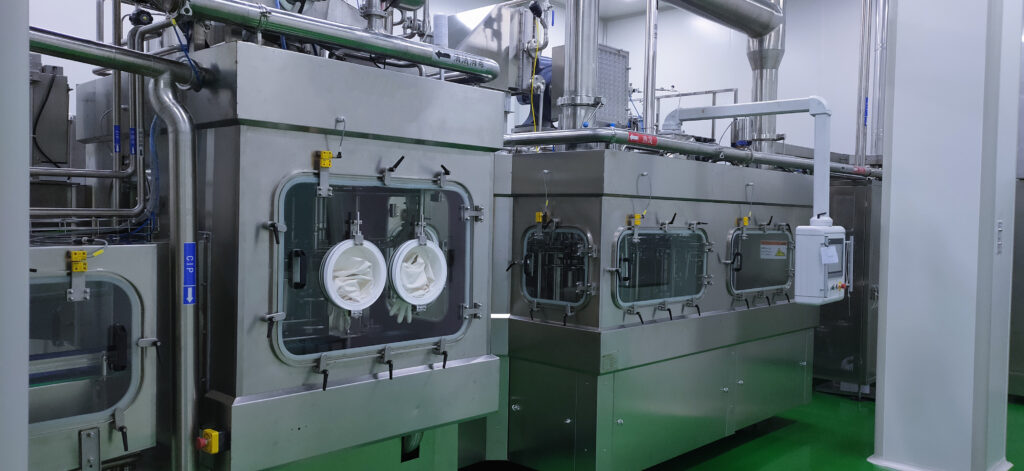

Key Features of the Filling Environment
- Closed Chamber: Physical barrier to contaminants.
- HEPA Filters: Removing airborne particles.
- Positive Pressure: Preventing air inflow.
- Automated Systems: Minimizing human contact.
- Continuous Monitoring: Ensuring sterility.
- Regular Sanitization: Maintaining cleanliness.
Dive deeper Paragraph:
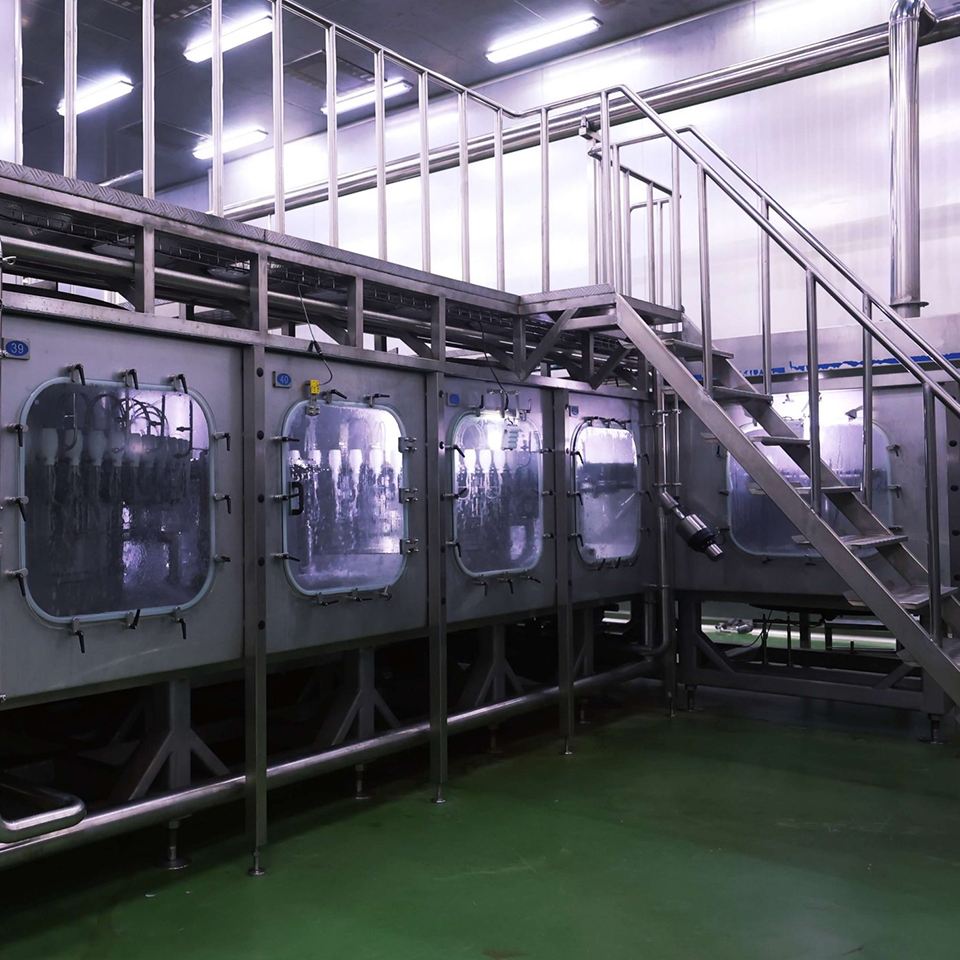
The heart of the aseptic filling process is the filling stage, where the sterilized product is transferred into the sterilized container within a completely sterile environment. This is typically achieved by performing the filling process within a closed chamber that is equipped with HEPA filters to remove airborne particles and maintain a sterile atmosphere. The chamber is also maintained at a positive pressure to prevent any air from flowing into the chamber, further reducing the risk of contamination.
Step 4: Sealing the Container
leading paragraph:
How do they seal the container to keep it sterile?
snippet paragraph:
Immediately after filling, the container is sealed to prevent any microorganisms from entering. The sealing process must also be sterile to maintain the product's safety and extend its shelf life.
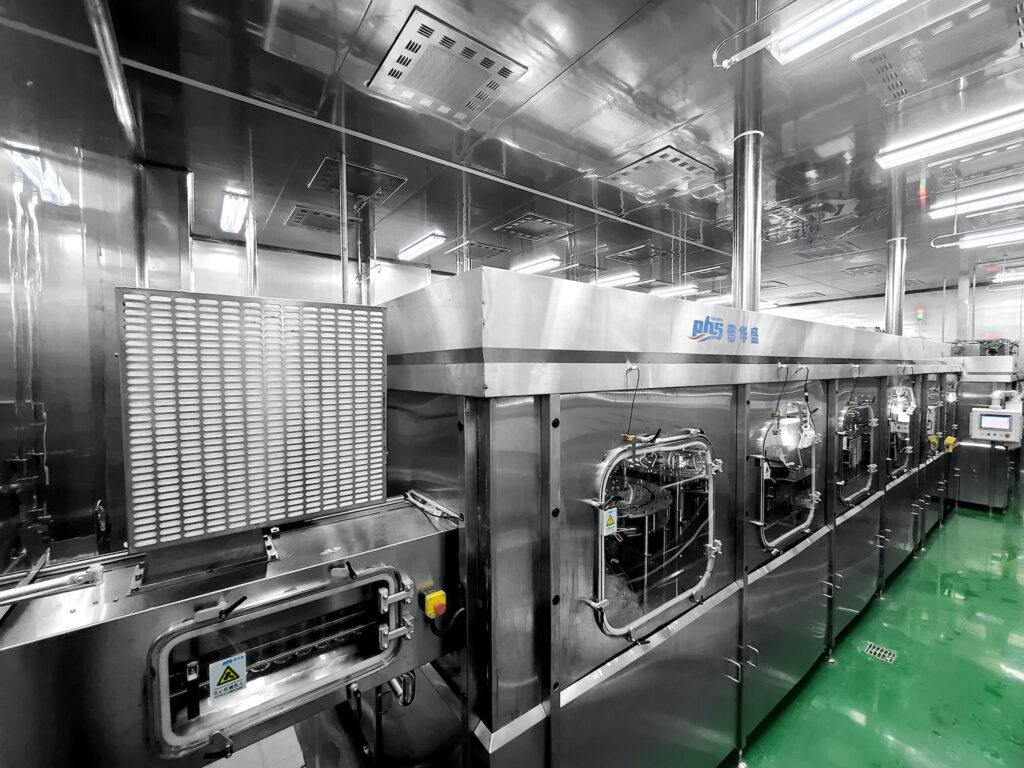

Sealing Techniques
- Heat Sealing: Melting the materials together.
- Ultrasonic Sealing: Using vibrations to bond.
- Induction Sealing: Creating a hermetic seal.
- Sterile Closures: Ensuring hygiene.
- Tamper-Evident Seals: Guaranteeing safety.
- Quality Checks: Verifying integrity.
Dive deeper Paragraph:
The final step in the aseptic filling process is to seal the container immediately after filling to prevent any microorganisms from entering and compromising the sterility of the product. The sealing process must also be sterile to maintain the integrity of the aseptic system. Various sealing techniques are used, depending on the type of packaging material and the specific requirements of the product.
Benefits of Aseptic Filling: Why It Matters
leading paragraph:
What are the advantages of using aseptic filling?
snippet paragraph:
Aseptic filling extends shelf life without refrigeration, preserves product quality and nutritional value, reduces the need for preservatives, and allows for wider distribution to areas with limited cold storage.

Key Advantages Summarized
- Longer Shelf Life: Reduced spoilage.
- Better Quality: Preserved nutrients.
- Fewer Preservatives: Healthier products.
- Wider Distribution: Reaching more consumers.
- Reduced Costs: Lower storage expenses.
- Sustainable Practices: Less waste.
Dive deeper Paragraph:
Aseptic filling offers a wide range of benefits for both food and beverage manufacturers and consumers. One of the most significant advantages is the extended shelf life of the products, which can be several months or even years without the need for refrigeration. This is particularly beneficial for distributing products to remote locations or regions where cold chain infrastructure is limited.
Conclusion
Aseptic filling might sound complex, but it's all about keeping things sterile! It's a fantastic way to ensure safe, high-quality food and beverages reach consumers everywhere.






