What Are the Key Elements That Impact the Beer Filling Process?
Leading paragraph:
Ever wondered what makes the perfect pour of beer? It's more than just tilting the glass right!
Snippet paragraph:
Key elements impacting beer filling include CO₂ control, hygiene, oxygen management, and proper equipment operation. These factors ensure consistent carbonation, prevent contamination, minimize oxidation, and maintain efficient production.

Transition Paragraph:
Let's dive into these elements to understand how each one contributes to a quality beer filling process.
What Are the Four Elements of Beer?
Leading paragraph:
Think of beer like a recipe – you need the right ingredients to make it great!
Snippet paragraph:
The four key elements of beer are water, malt, hops, and yeast. Water is the main component, malt provides sugars, hops add bitterness and aroma, and yeast ferments the sugars into alcohol and CO₂. Each plays a critical role in the beer's final character.
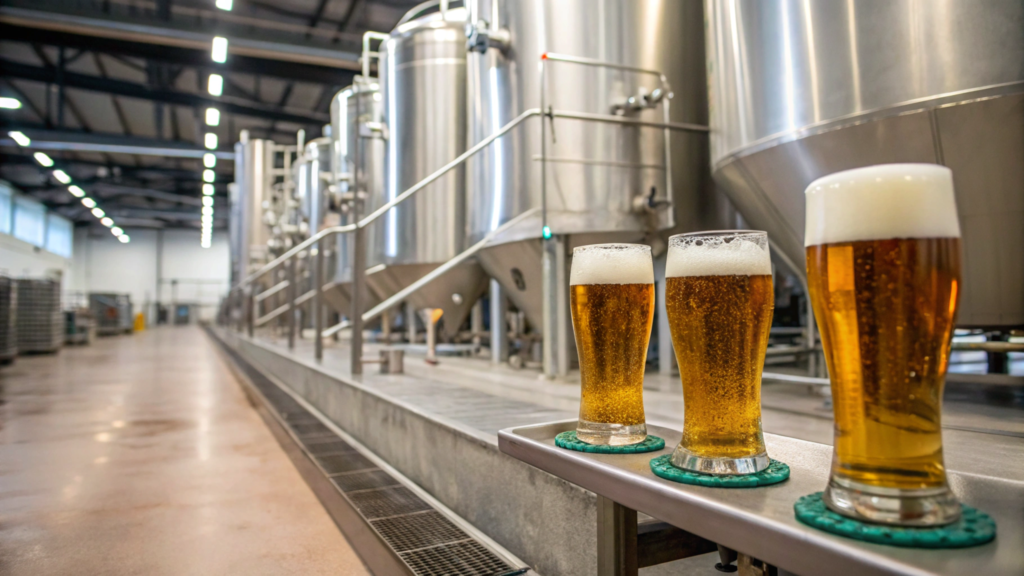

Dive deeper Paragraph:
Let's break down each element to understand its role:
Water
Water makes up about 90-95% of beer. The mineral content of water can significantly affect the beer's flavor and style. For example, hard water is suitable for dark beers, while soft water is better for light beers. The water must be free from impurities and contaminants.
Malt
Malt, usually barley, provides the sugars that yeast ferments into alcohol and CO₂. The type of malt used influences the beer's color, body, and flavor. Different malts can impart flavors ranging from biscuit and caramel to chocolate and roasted coffee.
Hops
Hops are flowers that add bitterness, aroma, and flavor to beer. They also act as a preservative. Different hop varieties offer a wide range of aromas, including floral, citrus, pine, and earthy notes. The timing of hop additions during brewing affects the beer's bitterness and aroma.
Yeast
Yeast is a microorganism that ferments the sugars from malt into alcohol and CO₂. Different yeast strains produce different flavors and aromas. Ale yeasts ferment at warmer temperatures and produce fruity esters. Lager yeasts ferment at cooler temperatures and produce clean, crisp flavors.
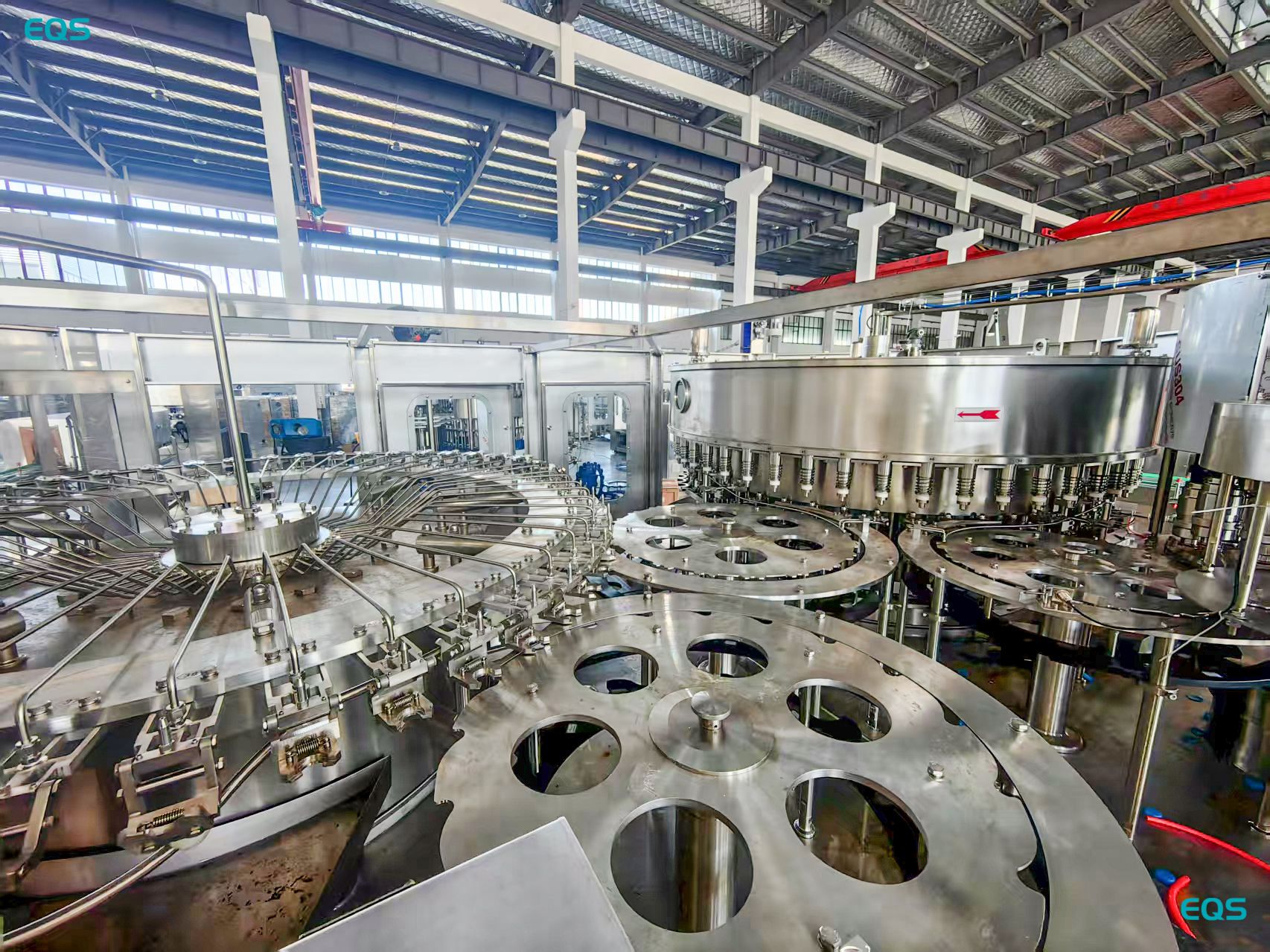
What Is the Working Principle of a beer filling machine
?
Leading paragraph:
Imagine a machine that precisely fills beer bottles without losing any fizz. That's the magic of a beer filling machine!
Snippet paragraph:
A beer filling machine works by using counter pressure to balance the pressure inside the bottle with the filling tank. This minimizes foaming and CO₂ loss. The machine fills the bottle, seals it, and then releases the pressure.
Dive deeper Paragraph:
Here's a detailed look at how the filling machine works:
Bottle Preparation
The process begins with cleaning and sanitizing the bottles. Bottles are inverted and rinsed with water or a sanitizing solution to remove any contaminants. Cleanliness is essential to prevent spoilage and maintain the beer's quality.
Pre-Purging
Before filling, the bottles are pre-purged with CO₂ to remove oxygen. Oxygen can negatively affect the beer's flavor and stability, leading to oxidation. By replacing oxygen with CO₂, the beer's freshness and carbonation are preserved.
Filling
The filling process utilizes counter pressure to minimize foaming and CO₂ loss. The machine equalizes the pressure inside the bottle with the pressure in the filling tank. Beer flows into the bottle through a filling valve, maintaining consistent pressure.
Snifting
Snifting is a process where a small amount of CO₂ is released from the bottle after filling. This process removes any remaining air in the bottle's headspace, ensuring a proper seal.
Capping
After filling and snifting, the bottles are immediately capped to seal in the carbonation and protect the beer from oxygen. The capping machine applies caps securely to prevent leaks and maintain the beer's quality.
What Are the Key Components of Beer?
Leading paragraph:
Besides the main ingredients, beer contains several other important components that contribute to its overall character.
Snippet paragraph:
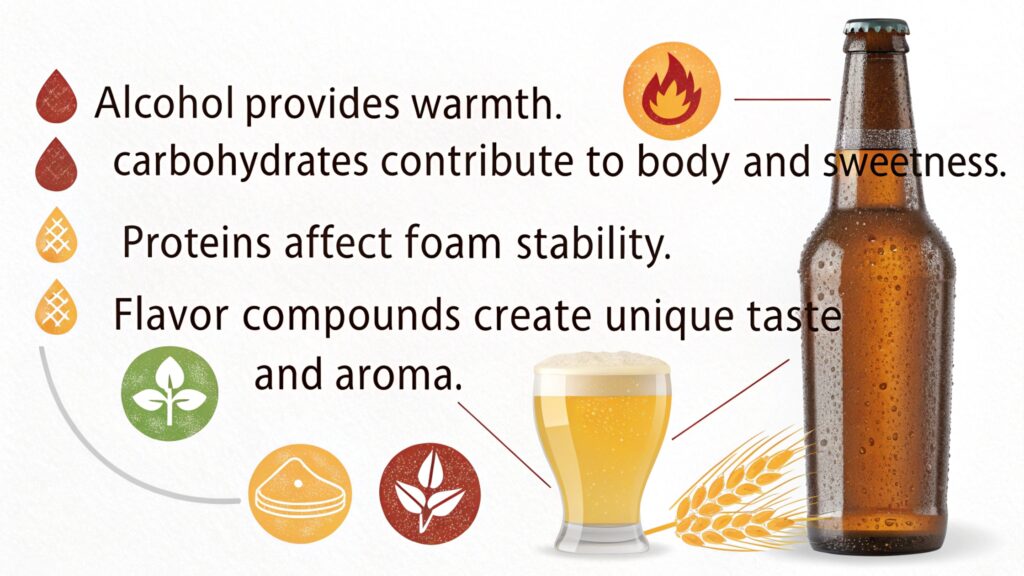
Key components of beer include alcohol, carbohydrates, proteins, and various flavor compounds. Alcohol provides the beer's characteristic warmth. Carbohydrates contribute to its body and sweetness. Proteins affect its foam stability. Flavor compounds create its unique taste and aroma.
Dive deeper Paragraph:
Let's explore these components:
Alcohol
Ethanol is produced by yeast fermentation. Alcohol content ranges from 3% to 12% ABV (alcohol by volume). It contributes to the beer's overall flavor profile.
Carbohydrates
These are primarily sugars that weren't fermented by the yeast. They add to the beer's body and sweetness. Different types of sugars affect the beer's mouthfeel.
Proteins
Proteins contribute to foam stability and can affect the beer's clarity. High protein content can lead to a hazy appearance. Brewers use fining agents to reduce protein levels and improve clarity.
Flavor Compounds
These include esters, phenols, and other aromatic compounds. They create the beer's unique taste and aroma. Different yeast strains and brewing techniques can influence the types and amounts of flavor compounds produced.
What Are the Primary Components of Wort That Are Crucial for the Beer Brewing Process?
Leading paragraph:
Wort is the liquid extracted from the mashing process that contains the sugars needed for fermentation.
Snippet paragraph:
The primary components of wort include sugars (primarily maltose), amino acids, vitamins, and minerals. Sugars are essential for fermentation. Amino acids provide nutrients for the yeast. Vitamins and minerals support yeast health and growth.

Dive deeper Paragraph:
Let's take a closer look:
Sugars
Maltose is the most abundant sugar in wort. Other sugars include glucose, fructose, and sucrose. The sugar profile affects the beer's fermentability, alcohol content, and residual sweetness.
Amino Acids
These are building blocks for proteins and are essential for yeast growth and metabolism. They also contribute to the beer's flavor and aroma. Different malts contain different levels of amino acids.
Vitamins
Wort contains several vitamins, including B vitamins. These vitamins support yeast health and fermentation efficiency. Brewers sometimes add supplemental vitamins to ensure optimal yeast performance.
Minerals
Minerals such as zinc, calcium, and magnesium are present in wort. These minerals play a role in yeast metabolism and enzyme activity. The mineral content of brewing water can affect the wort's mineral composition.
The most important thing I've learned is to control every step. For example, controlling the CO2 level, if you do not pay attention to that, the beer will lose the flavor.
Conclusion
Mastering the beer filling process involves a careful balance of ingredients, techniques, and equipment. By focusing on CO₂ control, hygiene, oxygen management, and understanding the key components, you can ensure a perfect pour every time.
My name is Allen, and I'm an expert in filling machine technology at EQS (eqsfilling.com), a leading liquid packaging solution provider based in China. If you're looking for top-quality equipment for your production line, feel free to reach out to me at [email protected]. We specialize in providing customizable solutions with cutting-edge technology.






